Introduction:
In the ever-evolving landscape of technology, one paradigm has emerged as a transformative force, revolutionizing the way businesses operate and individuals interact with information – Cloud-Based Software Solutions. This article embarks on a deep dive into the world of cloud-based software solutions, unraveling its intricacies, benefits, challenges, and the profound impact it has on businesses and the global technological ecosystem.
I. Benefits of Cloud-Based Software Solutions
Cloud-based software solutions have become a cornerstone for businesses seeking to leverage technology for enhanced efficiency, flexibility, and innovation. The benefits of adopting cloud-based software are multifaceted, ranging from cost savings to improved collaboration. In this section, we explore the key advantages that businesses can derive from embracing cloud technology.
- Cost-Efficiency:
- Reduced Capital Expenditure: Cloud-based solutions eliminate the need for businesses to invest heavily in on-premise hardware and infrastructure. Instead, they can leverage the resources provided by cloud service providers, paying for what they use.
- Operational Cost Savings: Cloud services offer a pay-as-you-go model, allowing businesses to scale resources up or down based on demand. This flexibility optimizes operational costs and prevents over-provisioning of resources.
- Scalability and Flexibility:
- On-Demand Resource Allocation: Cloud solutions provide businesses with the ability to scale resources up or down according to demand. This ensures that organizations can adapt quickly to changing needs, whether it be an increase in users, data storage requirements, or computing power.
- Global Accessibility: Cloud-based software allows employees to access applications and data from anywhere in the world, promoting remote work and enabling teams to collaborate seamlessly.
- Enhanced Collaboration:
- Real-Time Collaboration: Cloud-based collaboration tools facilitate real-time communication and collaboration among team members. Multiple users can work on documents simultaneously, fostering productivity and teamwork.
- Unified Access to Data: With data stored in the cloud, teams can access the latest information from a centralized location, reducing the risk of version control issues and ensuring that everyone works with up-to-date data.
- Security and Reliability:
- Data Encryption and Compliance: Cloud service providers implement robust security measures, including data encryption and compliance certifications. This ensures that sensitive business data is protected, and regulatory requirements are met.
- High Availability and Disaster Recovery: Cloud-based solutions often include built-in redundancy and disaster recovery capabilities. This ensures high availability, minimizing downtime and ensuring business continuity in the face of unexpected events.
- Automatic Updates and Maintenance:
- Streamlined Software Updates: Cloud-based software providers handle updates and maintenance, ensuring that businesses always have access to the latest features and security patches without the need for manual intervention.
- Reduced IT Workload: With infrastructure management handled by the cloud provider, internal IT teams can focus on strategic initiatives rather than routine maintenance tasks.
- Improved Innovation and Time-to-Market:
- Rapid Deployment of Solutions: Cloud platforms enable rapid deployment of applications and services, reducing time-to-market for new products or features.
- Access to Cutting-Edge Technologies: Cloud providers often integrate emerging technologies such as artificial intelligence, machine learning, and IoT, allowing businesses to leverage these innovations without extensive upfront investments.
- Eco-Friendly Practices:
- Energy Efficiency: Cloud providers are increasingly adopting sustainable practices, such as energy-efficient data centers and the use of renewable energy sources. Businesses leveraging cloud solutions contribute to a more eco-friendly IT landscape.
- Customer Satisfaction and Competitiveness:
- Improved Customer Experiences: Cloud-based solutions can enhance customer experiences through faster response times, personalized services, and reliable access to information.
- Competitive Edge: Businesses that embrace cloud technology gain a competitive edge by being more agile, innovative, and adaptable to market changes compared to those relying on traditional on-premise solutions.
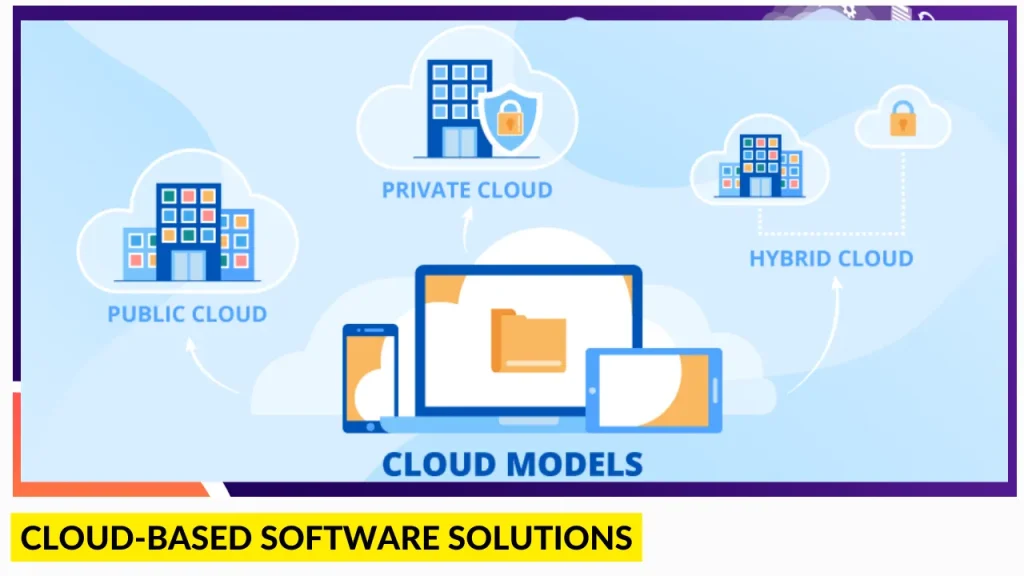
II. Understanding Cloud-Based Software Solutions:
- Definition and Evolution:
- Defining cloud-based software solutions.
- A historical overview of the evolution of cloud computing.
- The transition from on-premise to cloud-based solutions.
- Core Components:
- Infrastructure as a Service (IaaS).
- Platform as a Service (PaaS).
- Software as a Service (SaaS).
- The role of virtualization in cloud solutions.
III. Key Features and Advantages:
- Scalability:
- Exploring the scalability of cloud-based solutions.
- Elasticity and its significance for businesses.
- Case studies illustrating successful scalability in real-world applications.
- Cost-Efficiency:
- Analyzing the cost benefits of cloud-based software solutions.
- A comparison of traditional on-premise costs vs. cloud-based costs.
- Cost optimization strategies for leveraging cloud services effectively.
- Accessibility and Collaboration:
- The role of cloud solutions in fostering remote work.
- Enhanced collaboration through cloud-based platforms.
- Real-time access to data and applications from anywhere in the world.
- Security and Compliance:
- Addressing security concerns associated with cloud computing.
- Compliance regulations and the role of cloud providers.
- Best practices for ensuring data security in the cloud.
IV. Applications Across Industries:
- Healthcare:
- Cloud solutions in electronic health records (EHR) management.
- Telemedicine and the role of cloud infrastructure.
- Enhancing healthcare analytics through cloud-based platforms.
- Finance:
- The adoption of cloud-based financial management systems.
- Cloud solutions for risk management and compliance.
- The impact of cloud computing on fintech innovation.
- Education:
- Cloud-based learning management systems (LMS).
- Remote education and collaborative tools in the cloud.
- Analytics and personalized learning through cloud solutions.
- Manufacturing:
- The role of cloud-based solutions in smart manufacturing.
- Supply chain optimization through cloud technology.
- Predictive maintenance and IoT integration in manufacturing processes.
V. Challenges and Concerns:
- Data Privacy:
- Addressing concerns related to data privacy in the cloud.
- The role of encryption and secure access controls.
- Compliance with international data protection regulations.
- Downtime and Reliability:
- Analyzing the potential for downtime in cloud services.
- Strategies for ensuring high availability and reliability.
- Case studies of businesses mitigating downtime risks through cloud solutions.
- Vendor Lock-In:
- Understanding the concept of vendor lock-in.
- Strategies for avoiding vendor dependence in cloud services.
- Evaluating multi-cloud and hybrid cloud approaches.
- Integration Complexity:
- Challenges in integrating cloud solutions with existing infrastructure.
- Best practices for seamless integration and interoperability.
- The role of APIs in simplifying cloud integration.
VI. Future Trends and Innovations:
- Edge Computing:
- The emergence of edge computing in conjunction with cloud solutions.
- Edge vs. Cloud: Finding the right balance.
- Real-world applications and use cases of edge computing in cloud environments.
- Artificial Intelligence and Machine Learning:
- The integration of AI and ML into cloud-based platforms.
- Cloud-based services for training and deploying machine learning models.
- The impact of AI-driven automation on cloud operations.
- Quantum Computing:
- The potential of quantum computing in revolutionizing cloud services.
- Cloud platforms preparing for the quantum era.
- Exploring quantum-safe encryption in the cloud.
- Sustainable Cloud Computing:
- The environmental impact of cloud data centers.
- Green cloud initiatives and sustainable practices.
- The role of businesses in promoting eco-friendly cloud computing.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs) About Cloud-Based Software Solutions:
What is Cloud-Based Software?
Answer: Cloud-based software refers to applications and services that are hosted on remote servers and accessed over the internet. Instead of being installed on local devices, these solutions utilize cloud infrastructure for storage, processing, and delivery of data and services.
How does Cloud-Based Software differ from Traditional On-Premise Solutions?
Answer: Traditional on-premise solutions are installed and run on local devices and servers within an organization. In contrast, cloud-based software relies on remote servers managed by third-party providers, offering benefits such as scalability, accessibility, and cost-efficiency.
What are the Core Service Models in Cloud Computing?
Answer: The core service models in cloud computing are Infrastructure as a Service (IaaS), Platform as a Service (PaaS), and Software as a Service (SaaS). IaaS provides virtualized computing resources, PaaS offers a platform for application development, and SaaS delivers ready-to-use software applications.
How does Cloud Scalability Benefit Businesses?
Answer: Cloud scalability allows businesses to easily adjust their computing resources based on demand. This flexibility ensures efficient utilization of resources, prevents over-provisioning, and accommodates growth without the need for significant upfront investments.
What Security Measures are in Place for Cloud-Based Software Solutions?
Answer: Cloud providers implement robust security measures, including data encryption, access controls, identity management, and compliance certifications. Users are also responsible for implementing security best practices, such as secure authentication and regular audits.
What Challenges are Associated with Cloud Adoption?
Answer: Challenges include data privacy concerns, potential downtime, vendor lock-in, and integration complexities. Addressing these challenges requires careful planning, thorough risk assessment, and adopting strategies like multi-cloud approaches to mitigate risks.
How Can Businesses Ensure Data Privacy in the Cloud?
Answer: Businesses can ensure data privacy by implementing encryption for data at rest and in transit, establishing access controls, regularly updating security policies, and complying with relevant data protection regulations, such as GDPR or HIPAA.
What is Edge Computing, and How does it Relate to Cloud Solutions?
Answer: Edge computing involves processing data closer to the source of data generation, reducing latency and bandwidth usage. It complements cloud solutions by handling time-sensitive tasks at the edge while leveraging the cloud for more resource-intensive processing and storage.
What Strategies Exist to Avoid Vendor Lock-In with Cloud Services?
Answer: To avoid vendor lock-in, businesses can adopt multi-cloud or hybrid cloud strategies, ensuring that they are not reliant on a single cloud provider. Additionally, using standardized APIs and containerization technologies can enhance portability across different cloud environments.
How Can Cloud-Based Software Solutions Contribute to Sustainability?
Answer: Cloud providers are increasingly adopting sustainable practices, such as energy-efficient data centers and renewable energy sources. Businesses can contribute to sustainability by choosing eco-friendly cloud providers and optimizing their resource usage to reduce environmental impact.
Conclusion:
As we navigate the digital era, cloud-based software solutions stand as the bedrock of innovation, offering unparalleled scalability, accessibility, and collaboration.
This article has delved into the depths of cloud computing, examining its evolution, key features, industry applications, challenges, and future trends. Embracing cloud technology isn’t just a trend; it’s a strategic imperative for businesses aiming to thrive in the dynamic landscape of the 21st century.
The journey to the cloud is not without challenges, but the rewards in terms of efficiency, innovation, and competitiveness are undoubtedly worth the voyage.
